Notes
Transmission Media
Types of Transmission Media

- Guided media is physical which we can touch and have high speed.
- Unguided medi is wireless which we can’t see and have comparatively slow speed
Guided Media
Twisted pair cable

Twisted pair cabling is a type of wiring in which two conductors of a single circuit are twisted together for the purposes of improving electromagnetic compatibility. Compared to a single conductor or an untwisted balanced pair, a twisted pair reduces electromagnetic radiation from the pair and crosstalk between neighboring pairs and improves rejection of external electromagnetic interference. It was invented by Alexander Graham Bell.
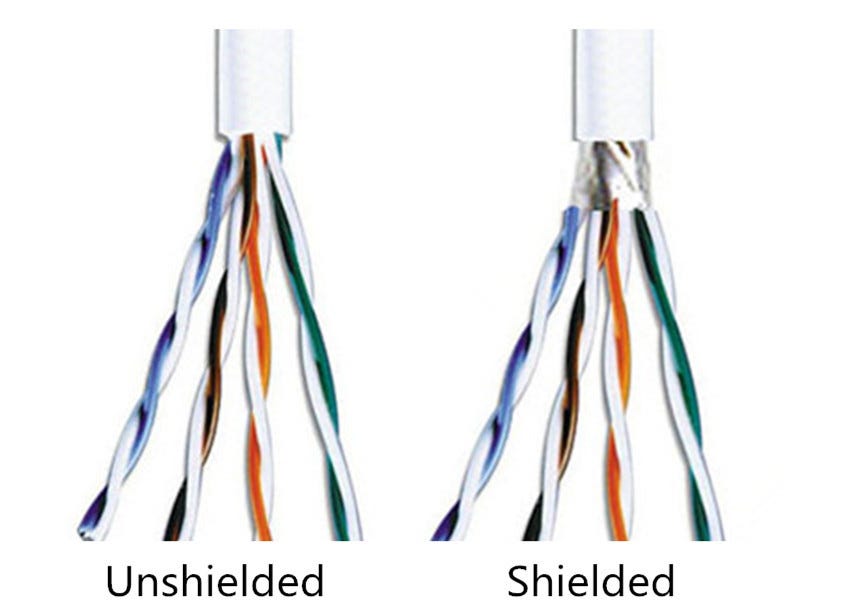
Two types:
- shielded twisted pair (STP)
- Shieled with plastic cover
- unshielded twisted pair (UTP)
- No shield
Coaxial Cable
Coaxial cable, or coax is a type of electrical cable consisting of an inner conductor surrounded by a concentric conducting shield, with the two separated by a dielectric (insulating material); many coaxial cables also have a protective outer sheath or jacket. The term “coaxial” refers to the inner conductor and the outer shield sharing a geometric axis.

Optical Fiber Cable
A fiber-optic cable, also known as an optical-fiber cable, is an assembly similar to an electrical cable, but containing one or more optical fibers that are used to carry light. The optical fiber elements are typically individually coated with plastic layers and contained in a protective tube suitable for the environment where the cable is used. Different types of cable are used for different applications, for example, long distance telecommunication, or providing a high-speed data connection between different parts of a building.
