Notes
Switching
What is switching
Switching is the practice of directing a signal or data element toward a particular hardware destination. Switching may be applied in various formats and can function in diverse ways within a greater network infrastructure.
Types of switching
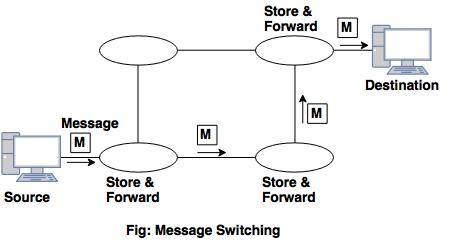
Message Switching
- Whole message is stored and transferred directly.
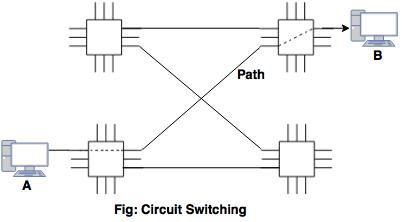
Circuit Switching
- Reserve the link between nodes and transfer data at same speed.
- Dedicated path is reserved and another path can’t be used.
- Physical layer
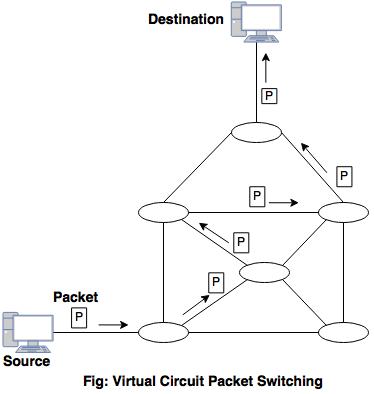
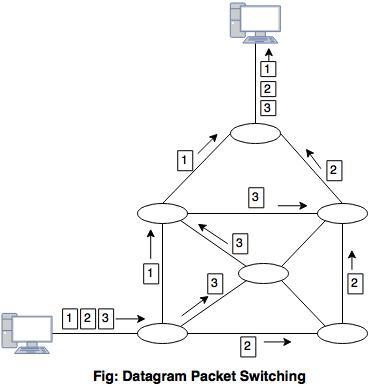
Packet Switching
- Path doesn’t matter , it just have to reach destination
- Data transferred in packets/frames
-
High efficiency
- Each packet carries a header that contains the full information about the destination.
- When the switch receives the packet, the destination address in the header of the packet is examined; the routing table is consulted to find the corresponding port through which the packet should be forwarded
- Virtual circuit packet switching establishes a fixed path between a source and a destination to transfer the packets.