Notes
Subnetting
What is subnetting?
A subnetwork or subnet is a logical subdivision of an IP network. The practice of dividing a network into two or more networks is called subnetting. Computers that belong to the same subnet are addressed with an identical most-significant bit-group in their IP addresses.
Logical subdivision of a network is called subnetting.
Why subnetting required?
- Security
- Similar IP address format
- saving IPv4 IP’s
- organizing network
- Reduce congestion
How to do subnetting?
Many methods are there but we are going to see only CIDR a.b.c.d / x is CIDR format (Classless inter domain routing) where a,b,c,d are octets and x is value that denotes common bits from left to right example : 192.168.0.1/24 -> 255 Devices can be identified Check IP for classes about subnetting in IP’s classes.
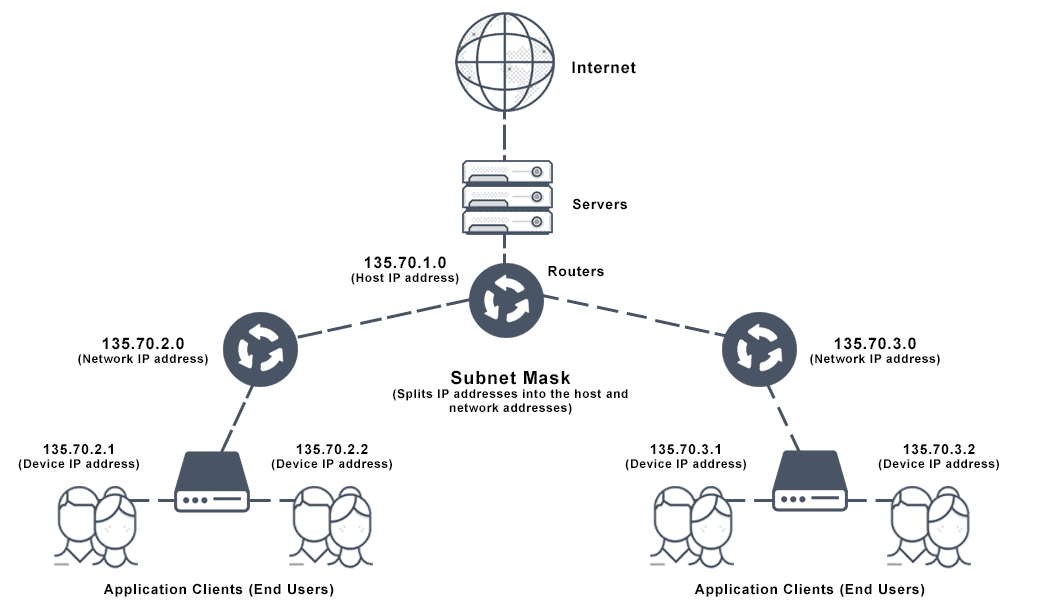
Common terms in subnetting
IF IP= 192.168.0.1/24
Broadcast ID/address A broadcast address is a network address used to transmit to all devices connected to a multiple-access communications network. A message sent to a broadcast address may be received by all network-attached hosts.The broadcast address is used by multiple protocols such as ARP, the Routing Information Protocol (RIP), and other protocols that must transmit data before they know the local subnet mask. Last IP address : 192.168.0.255
Network ID is the portion of an IP address that identifies the TCP/IP network on which a host resides. The network ID portion of an IP address uniquely identifies the host’s network on an internetwork, while the host ID portion of the IP address identifies the host within its network. First IP address : 192.168.0.0
Host Range Number of host that can connect to network is host range. Host range is always available IP - 2 . IP range : 192.168.0.1-192.168.0.254
Default gateway Default gateway is an IP address that traffic gets sent to when it’s bound for a destination outside the current network. Basically IP of router IP : 192.168.0.1 ( generally at start of possible )
VLSM
Variable Length Subnetting Mask IP blocks are divided even further and length of network id varies.