Notes
BGP
What is BGP?
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is a standardized exterior gateway protocol designed to exchange routing and reachability information among autonomous systems (AS) on the Internet. BGP is classified as a path-vector routing protocol and it makes routing decisions based on paths, network policies, or rule-sets configured by a network administrator.
BGP used for routing within an autonomous system is called Interior Border Gateway Protocol, Internal BGP (iBGP). In contrast, the Internet application of the protocol is called Exterior Border Gateway Protocol, External BGP (eBGP).
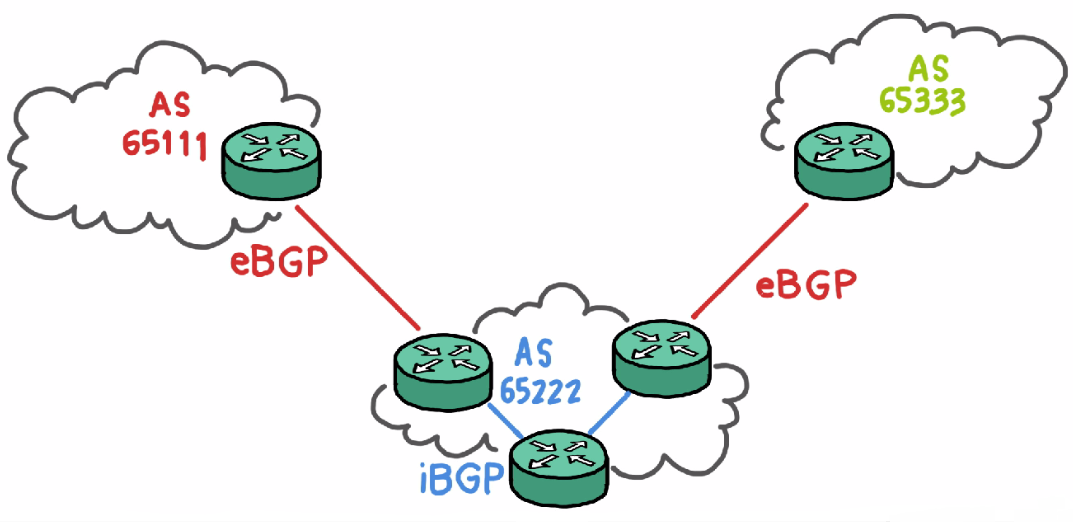
Point to point communication.
Working of BGP
BGP neighbors, called peers, are established by manual configuration among routers to create a TCP session on Ports 179. A BGP speaker sends 19-byte keep-alive messages every 30 seconds (protocol default value, tunable) to maintain the connection. Among routing protocols, BGP is unique in using TCP as its transport protocol.
Header of BGP
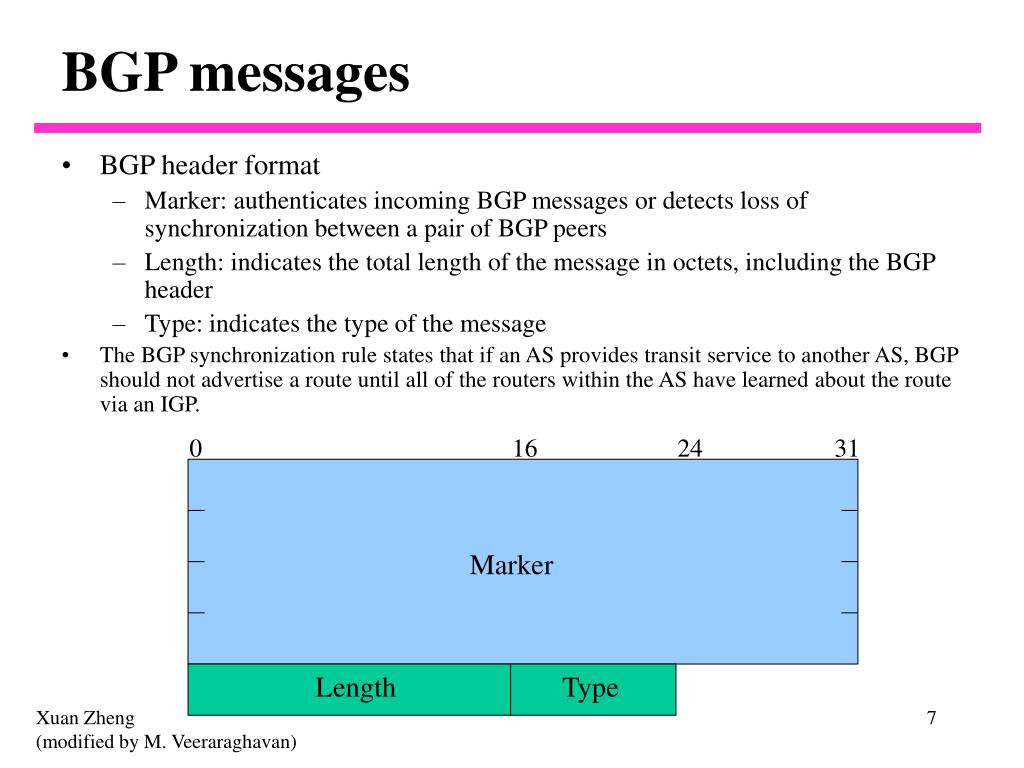
BGP Messages
|Message|Purpose| |:–|:–| |OPEN |Sets up and establishes BGP adjacency| |UPDATE|Advertises, updates, or withdraws routes| |NOTIFICATION|Indicates an error condition to a BGP neighbor| |KEEPALIVE|Ensures that BGP neighbors are still alive|